

Effects of pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on maternal and infant complications. Sun Y, Shen Z, Zhan Y, Wang Y, Ma S, Zhang S, et al. Impact of maternal body mass index and gestational weight gain on pregnancy complications: an individual participant data meta-analysis of European, north American and Australian cohorts. Santos S, Voerman E, Amiano P, Barros H, Beilin LJ, Bergström A, et al. Association of gestational weight gain with adverse maternal and infant outcomes. Voerman E, Santos S, Inskip H, Amiano P, Barros H, Charles MA, et al.
BODY MASS INDEX CALCULATOR NIH HOW TO
Additionally, women should be given general advice on how to achieve their ideal pre-pregnancy BMI and GWG.īody mass index gestational weight gain neurodevelopment obese overweight pre-pregnancy. In this study we found optimal GWG recommendations proposed by 2019 Life Cycle Project-Maternal Obesity and Childhood Outcomes Study Group were more suitable for Chinese women than 2009 Institute of Medicine(IOM) guidelines.
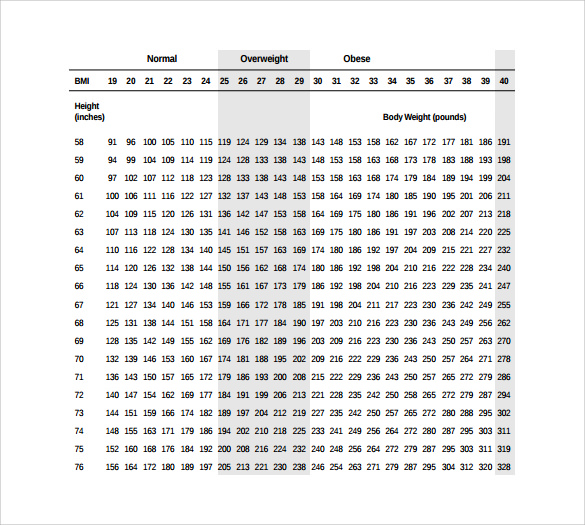
Such results are significant given the incidence of overweight and obesity as well as the long-term effects of early brain development. The PDI scores of the infants were not affected by the maternal pre-pregnancy BMI or GWG.įor Chinese babies aged 2 in this nationally representative sample, aberrant pre-pregnancy BMI and GWG can impair infants' mental development, but not psychomotor development. Meanwhile, we find among the normal pre-pregnancy BMI mothers, infants of inadequate GWG mothers had lower MDI scores ( β = -3.952, 95%CI = -7.809 to -0.094) compared with the referenced adequate GWG mothers, as well as the infants of excessive GWG mothers among the underweight pre-pregnancy BMI mothers ( β = -5.173, 95%CI = -9.803 to -0.543). Infants of overweight and obese moms exhibited lower MDI scores than those of mothers with normal pre-pregnancy BMI ( β = -2.510, 95%CI = -4.821 to -0.200) in the entire sample. The multivariate regression models were used to calculate the beta ( β) coefficients and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for estimating the associations between continuous Bayley scores and maternal pre-pregnancy BMI categories, as same as in GWG categories. The outcome was an assessment of child neural development at age 2 which was measured by employing a Chinese translation of the Bayley scales (BSID-CR). Based on the 2019 Life Cycle Project-Maternal Obesity and Childhood Outcomes Study Group, categories for GWG were created. The Chinese classification was used to group maternal BMI before conception. The study population was 3,115 mother-infant pairs were registered in the Wuhan Health Baby cohort between September 2013 and October 2018, and data from this cohort was used in this investigation. The current research investigates the associations among maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, GWG, and the risk of child neural development at 2 years of age depending on a Chinese birth prospective study. Only a few research have looked at the relationship between gestational weight growth and pre-pregnancy BMI in mothers and the neurobehavioral development of their infants. In recent decades, there has been a surge in both obesity and developmental impairments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
